
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. NASA have many launch facilities but most are inactive. The most commonly used pad will be LC-39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Spacecraft
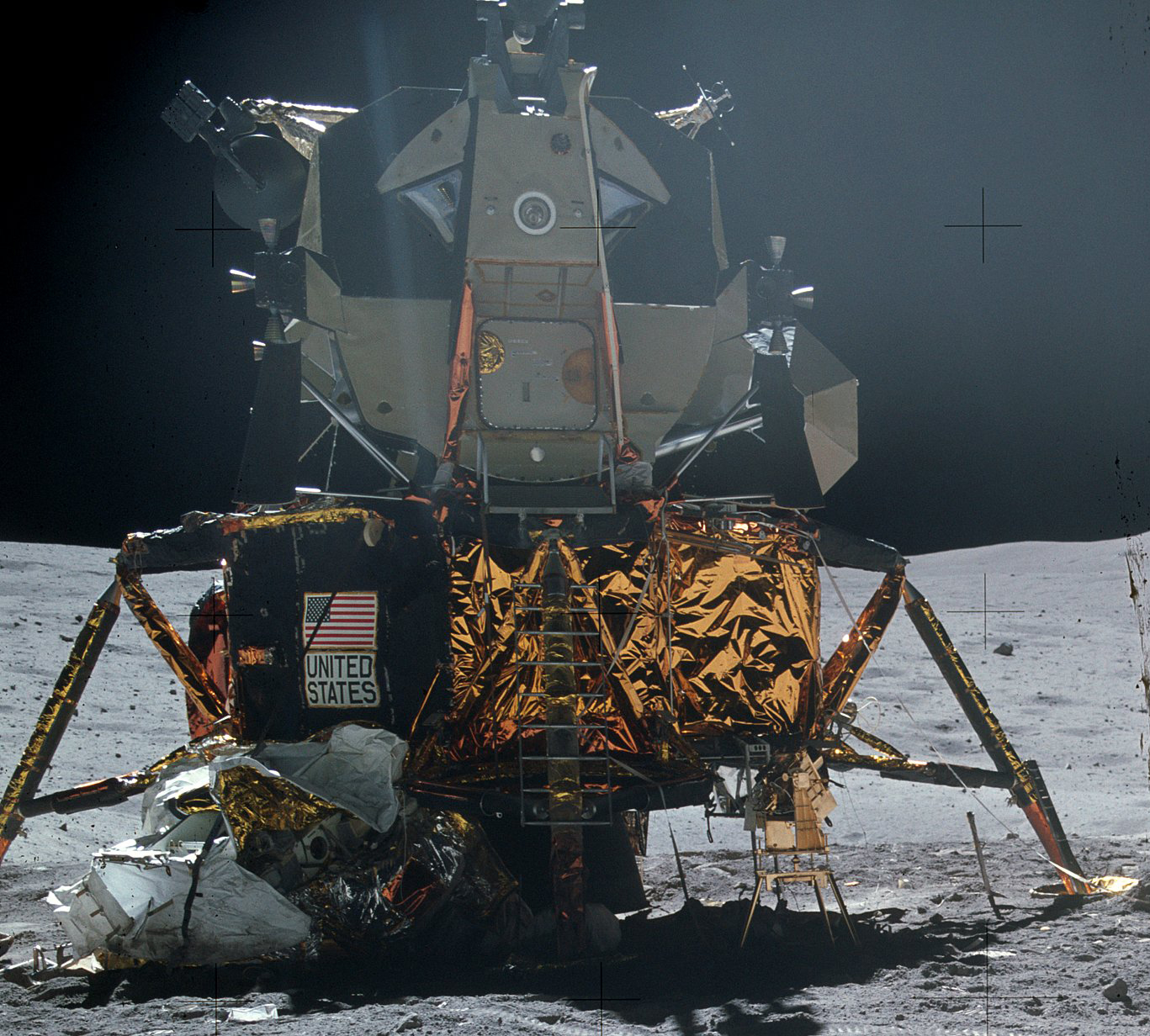

Type: Lander
Capability: Landing on the Moon, Rendezvous in lunar orbit
History: First flown in 1969, the LM achieved its historic moment on July 20th, 1969, when the "Eagle" landed on the Moon, carrying the first humans to walk on its surface.
Details: The Apollo Lunar Module was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed spacecraft to operate exclusively in the airless vacuum of space, and was the first crewed vehicle to land anywhere beyond Earth.
Maiden Flight: 1968-01-22
Height: 7.04 meters
Diameter: 4.22 meters
Payload Capacity: kg
Flight Life:
Wiki Link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apollo_Lunar_Module
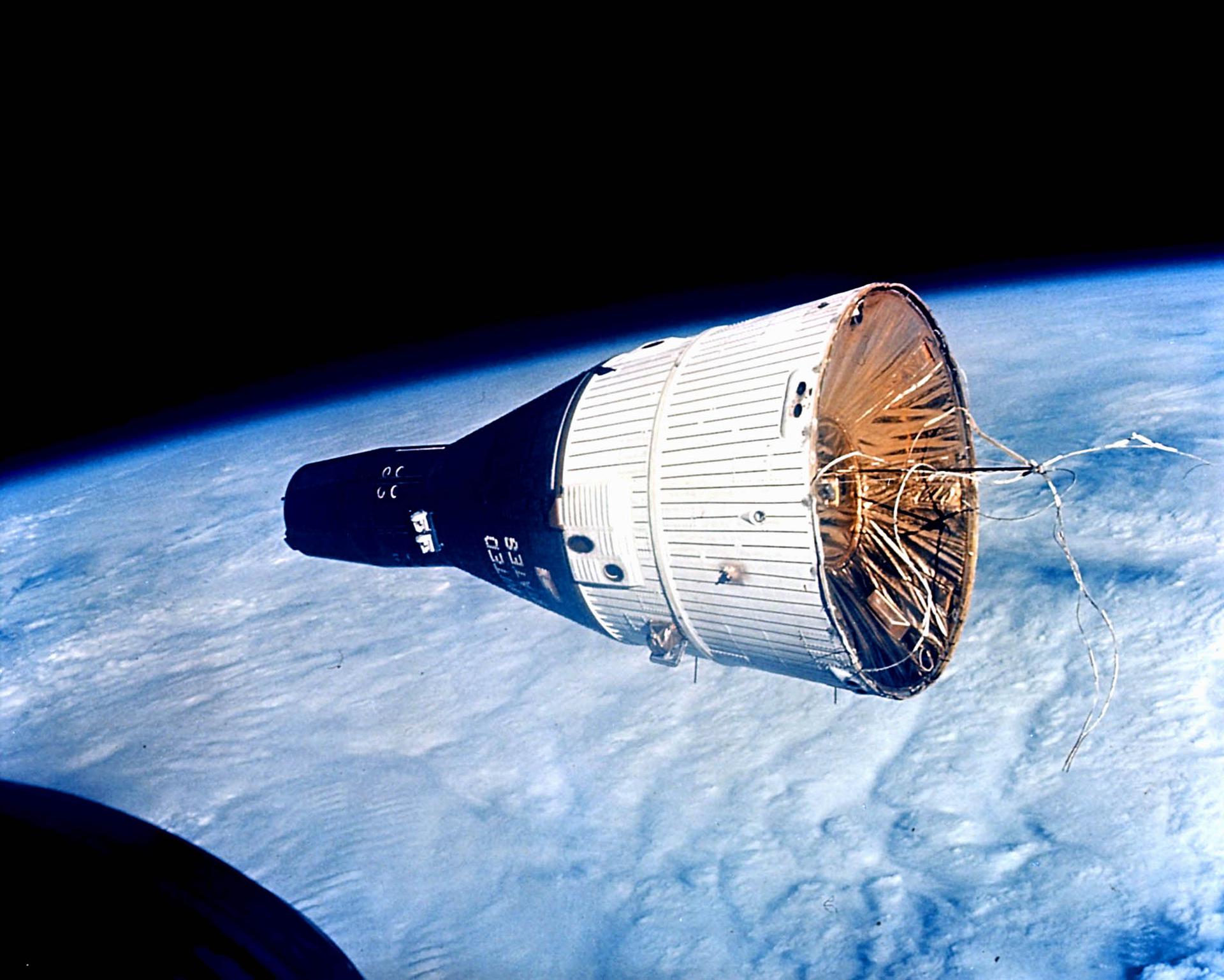

Type: Capsule
Capability: Human transportation to low Earth orbit.
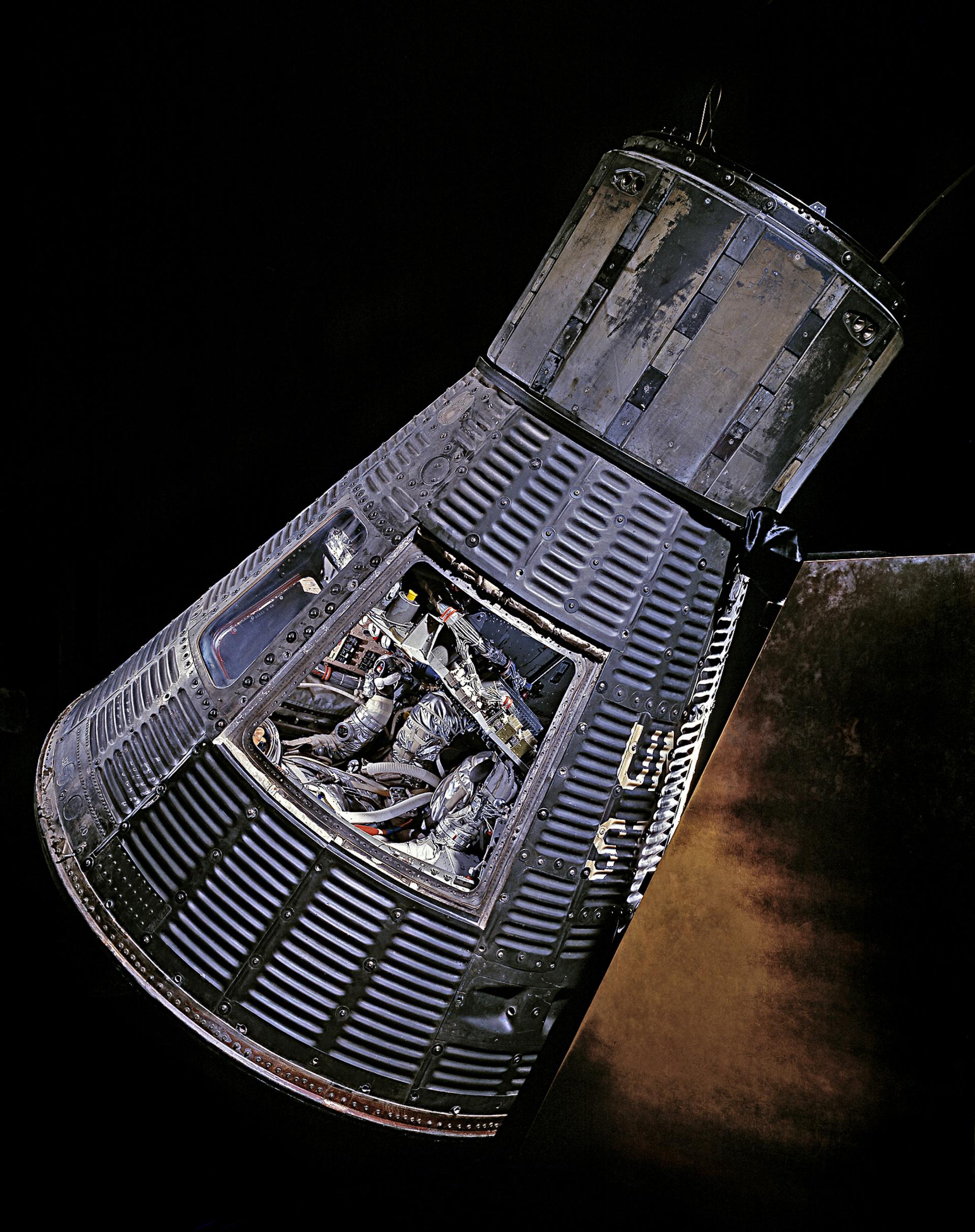
History: The Gemini crew capsule (referred to as the Reentry Module) was essentially an enlarged version of the Mercury capsule. Unlike Mercury, the retrorockets, electrical power, propulsion systems, oxygen, and water were located in a detachable Adapter Module behind the Reentry Module. A major design improvement in Gemini was to locate all internal spacecraft systems in modular components, which could be independently tested and replaced when necessary, without removing or disturbing other already tested components.
Details: The spacecraft was 18 feet 5 inches (5.61 m) long and 10 feet (3.0 m) wide, with a launch weight varying from 7,100 to 8,350 pounds (3,220 to 3,790 kg).
Maiden Flight: 1964-04-08
Height: 5.61 meters
Diameter: 3 meters
Payload Capacity: kg
Flight Life: Between a few hours and multiple days (14 day is the maximum achieved).
Wiki Link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_Gemini#Spacecraft
Type: Capsule
Capability: Human transportation to upper Earth atmosphere and low Earth orbit.
History: The Mercury spacecraft was the manned capsule used for suborbital and orbital launches during the Project Mercury, the first human spaceflight program of the United States, from 1958 through 1963.
Details: The Mercury spacecraft's principal designer was Maxime Faget, who started research for manned spaceflight during the time of the NACA. With 100 cubic feet (2.8 m3) of habitable volume, the capsule was just large enough for a single crew member. Inside were 120 controls: 55 electrical switches, 30 fuses and 35 mechanical levers. The heaviest spacecraft, Mercury-Atlas 9, weighed 3,000 pounds (1,400 kg) fully loaded. Its outer skin was made of René 41, a nickel alloy able to withstand high temperatures.
Maiden Flight: 1961-05-05
Height: 3.3 meters
Diameter: 1.8 meters
Payload Capacity: kg
Flight Life: Between 15 minutes and 3 days.
Wiki Link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_Mercury#Spacecraft
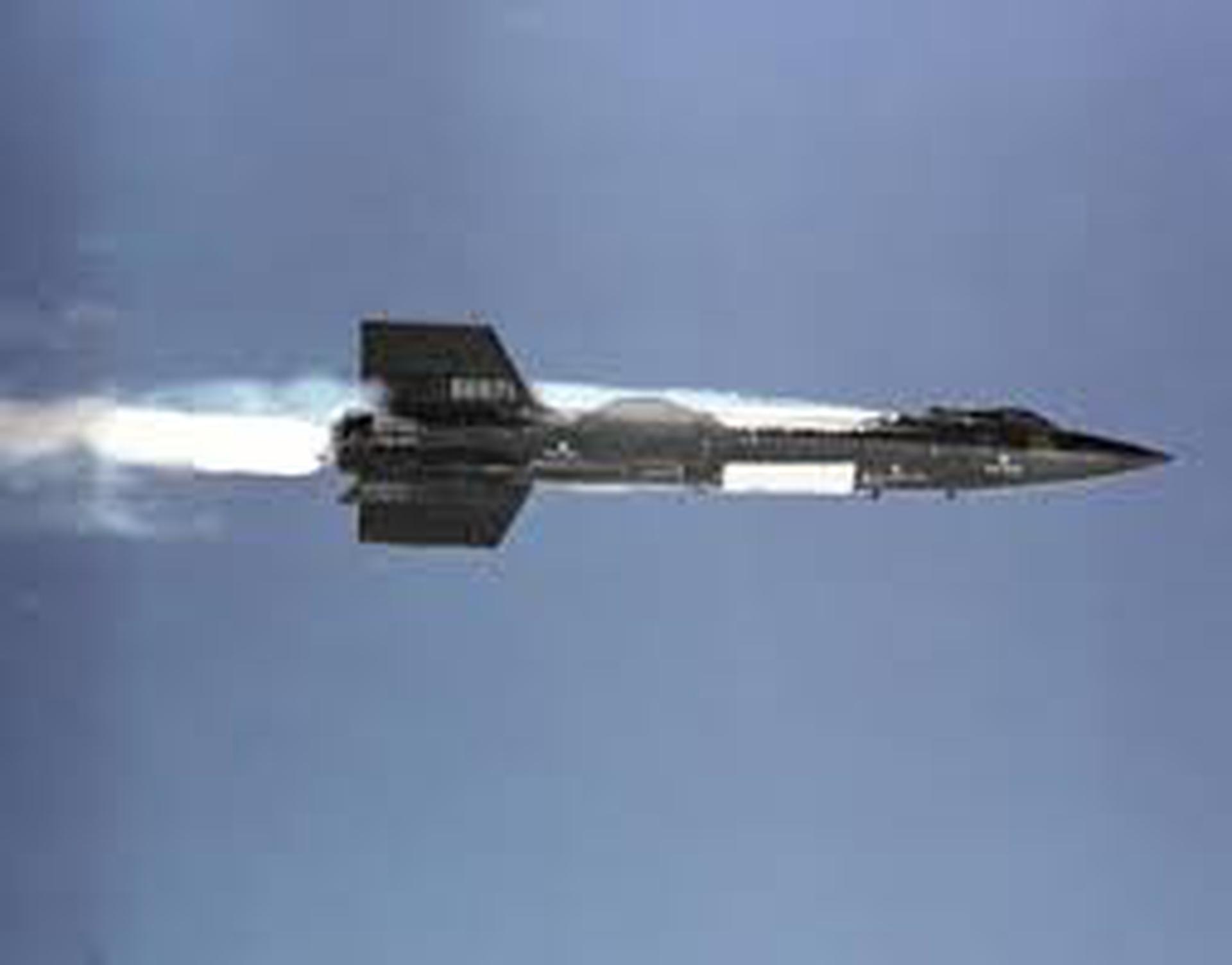

Type: Spaceplane
Capability: Experimental aircraft used for Aircraft and Spacecraft design
History: The North American X-15 currently holds the record for the highest speed in a manned, powered aircraft. The three variants of the X-15 flew nearly 200 times, with 13 of them going over 80km high.
Details: The North American X-15 was a hypersonic rocket-powered aircraft operated by the United States Air Force and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. The X-15 reached altitudes of over 80km and speeds of over 6000 km/h. The X-15 had a wingspan of 6.8 meters, and length of 15.4
Maiden Flight: 1959-06-08
Height: 15.45 meters
Diameter: 6.8 meters
Payload Capacity: kg
Flight Life: ~10 minute flights
Wiki Link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/North_American_X-15
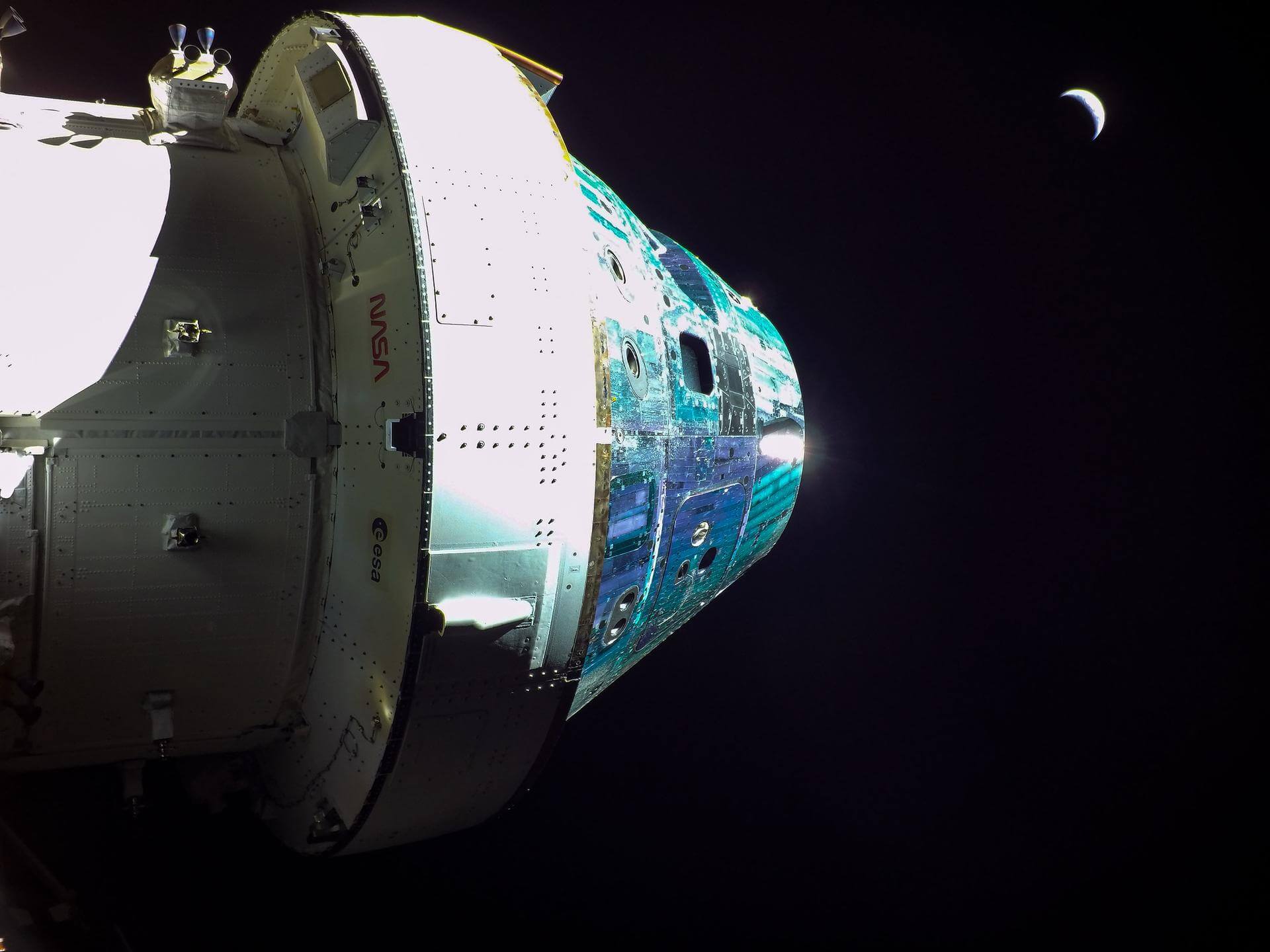

Type: Capsule
Capability: Lunar Missions.
History: The Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (Orion MPCV) is an American spacecraft intended to carry a crew of four astronauts to destinations at or beyond low Earth orbit (LEO). Currently under development by NASA for launch on the Space Launch System, Orion is intended to facilitate human exploration of asteroids and of Mars, as well as to provide a means of delivering or retrieving crew or supplies from the ISS if needed.
Details: The Orion MPCV takes basic design elements from the Apollo Command Module that took astronauts to the moon, but its technology and capability are more advanced. It is designed to support long-duration deep space missions, with up to 21 days active crew time plus 6 months quiescent. During the quiescent period crew life support would be provided by another module such as a Deep Space Habitat. The spacecraft's life support, propulsion, thermal protection and avionics systems are designed to be upgradeable as new technologies become available. nn The MPCV spacecraft includes both crew and service modules, and a spacecraft adaptor. The MPCV's crew module is larger than Apollo's and can support more crew members for short or long-duration missions. The service module fuels and propels the spacecraft as well as storing oxygen and water for astronauts. The service module's structure is also being designed to provide locations to mount scientific experiments and cargo.
Maiden Flight: 2022-11-16
Height: 3.3 meters
Diameter: 5.03 meters
Payload Capacity: 100 kg
Flight Life: 21.1 days
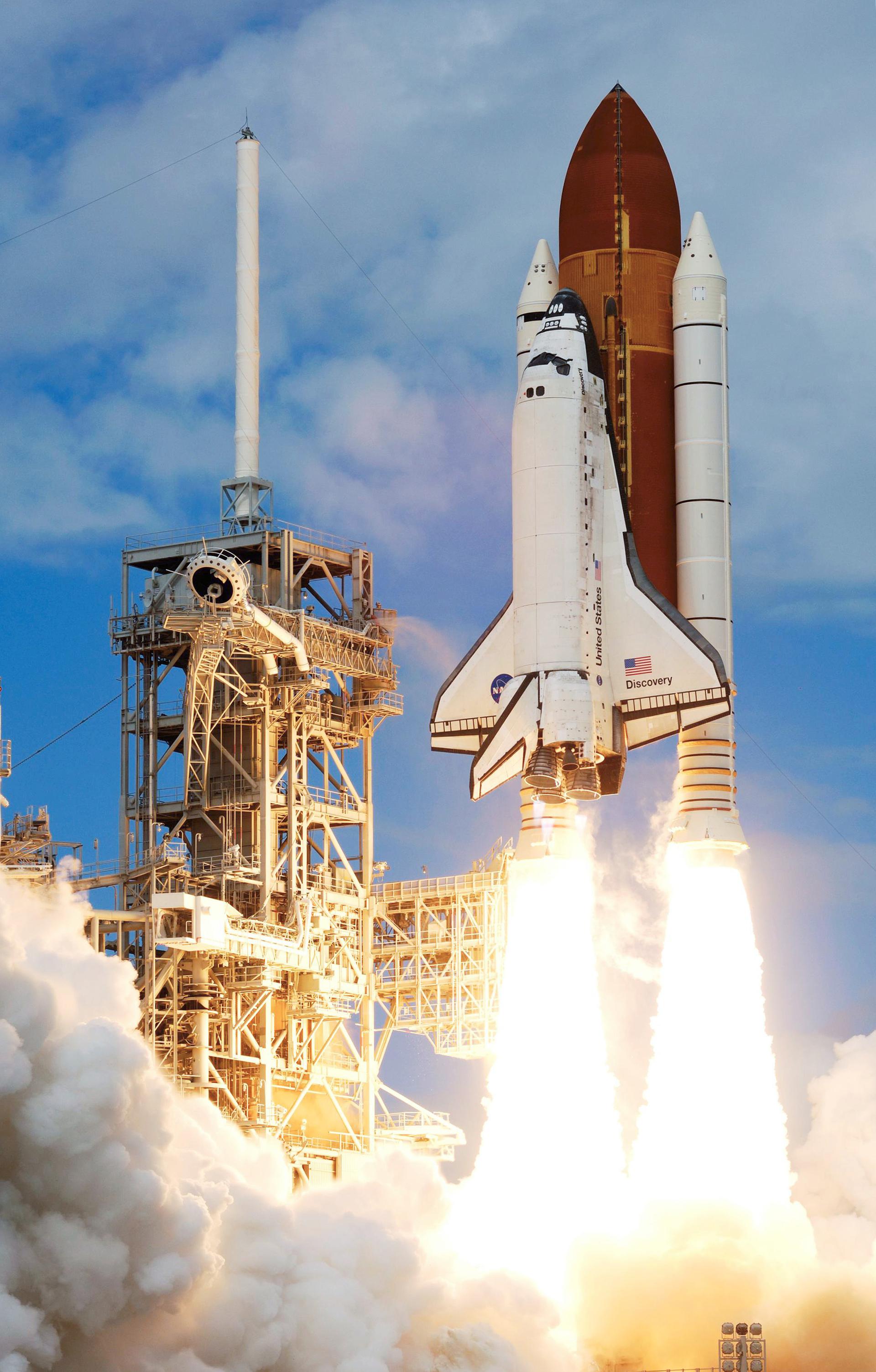

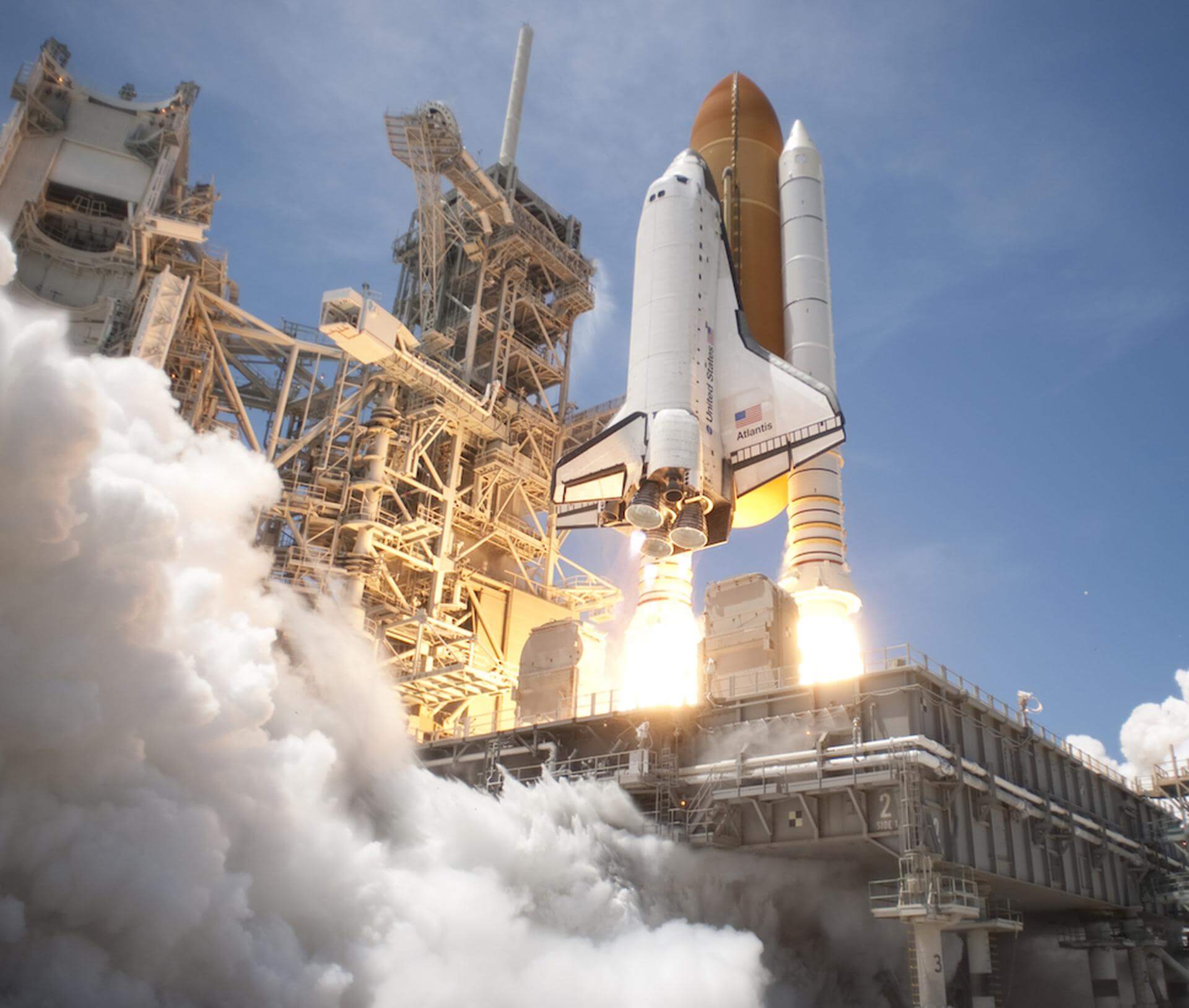
Type: Spaceplane
Capability: Carrying a crew of 7 astronauts along with cargo to Low Earth Orbit.
History: The Space shuttle was a United States space craft. Following the conclusion of the Apollo program the Space Shuttle intended to lower costs for reliable access to Low Earth Orbit. The program ran from 1981-2011.
Details: The Space Shuttle was a partially reusable LEO spacecraft system operated by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft of which it was the only item funded for development. The first of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights in 1982. In addition to the prototype whose completion was cancelled, five complete Shuttle systems were built and used on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST); conducted science experiments in orbit; and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station. The Shuttle fleet's total mission time was 1322 days, 19 hours, 21 minutes and 23 seconds.
Maiden Flight: 1981-04-12
Height: 56.1 meters
Diameter: 8.7 meters
Payload Capacity: 27500 kg
Flight Life: 14 days
Wiki Link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Space_Shuttle